Gingivitis: In the early stage of gingivitis, bacterial plaque accumulates, causing inflammation and bleeding of the gums during tooth brushing. Since bone and other tissue have not been seriously damaged, the teeth remain firmly planted in their sockets.
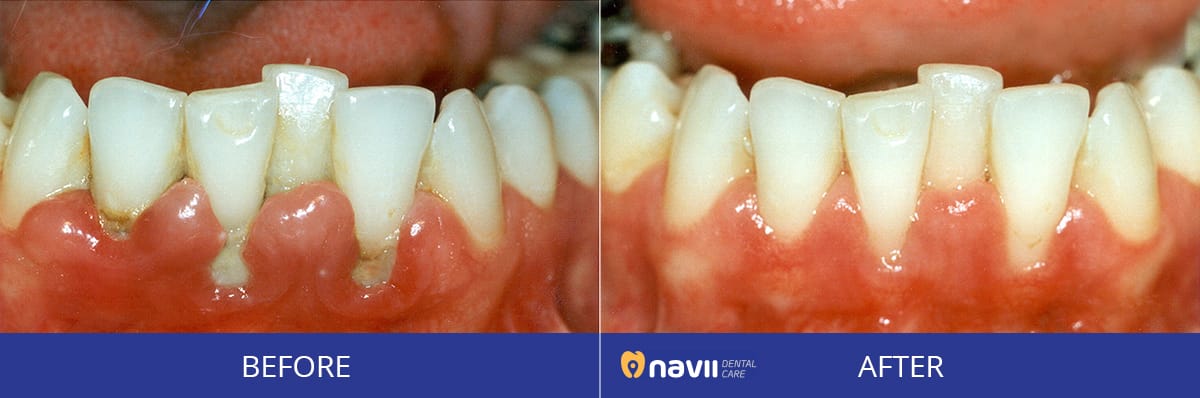
Periodontitis: If gingivitis is not treated, it can advance to periodontitis. In this stage, the plaque spreads and grows below the gum line. As the gums become inflamed and swollen, they detach from the teeth and form pockets, which collect food debris and can become infected. Signs and symptoms of periodontitis include persistent bad breath, receding gums, red and swollen gums, loose or sensitive teeth, and discomfort or pain when chewing.
Advanced periodontitis: As periodontitis develops, the pockets deepen, and toxins produced by bacteria and enzymes in these pockets start destroying more gum tissue, bone, and other periodontal structures. As teeth are no longer anchored in place, loose teeth or tooth loss may occur.
Periodontitis is an extremely common dental disease. Tobacco use and poor oral hygiene habits are typical causes of periodontitis. Other causes include hormonal changes, illnesses, medications, bad habits, and genetics.
You should visit a dental clinic if you encounter any of the signs and symptoms listed above. Our doctors will develop an appropriate treatment plan based on the stage of the disease. Gingivitis, the early stage of periodontitis, can be treated quickly if you follow good oral hygiene habits and have routine dental checkups. Periodontitis, the second stage, requires scaling and root planing to remove dental plaque and smooth out the root surfaces. If periodontitis progresses to an advanced stage, surgeries may be required.


 VI
VI